USB Power Delivery Tester PRO
For troubleshooting USB ports and USB chargers (Model: PM240)
Also available in a 100W model
- Test USB and Thunderbolt ports, chargers, and power banks by dissipating up to 240W to verify power output, voltage stability, and compliance with specifications.
- Check if a USB host can deliver its maximum specified wattage and its output voltage levels remain within specification under high load.
- Detect claimed wattage of chargers for optimized charging speeds and assess the true capacity of power banks under specific loads.
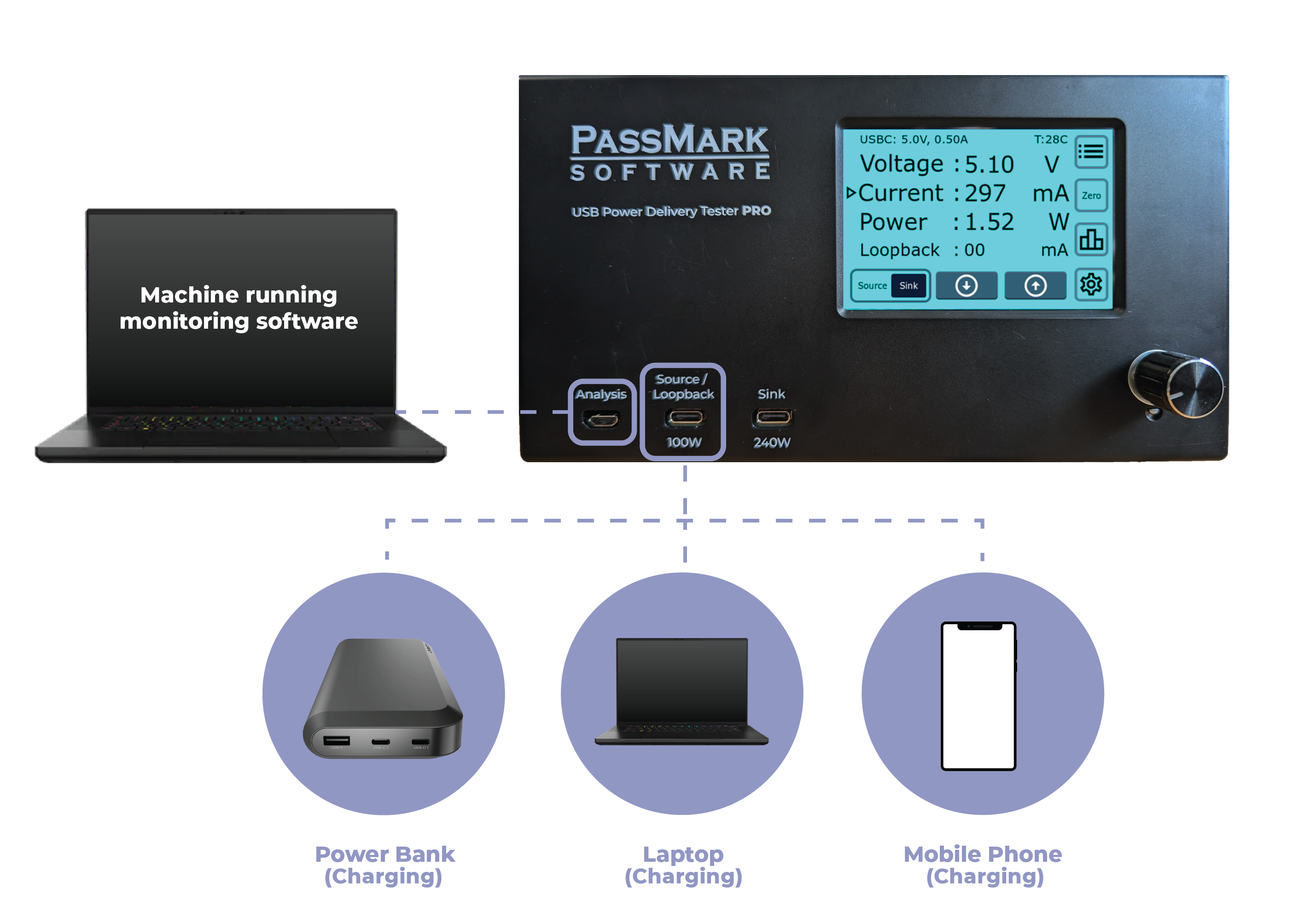
- Emulate USB chargers with a configurable 100W source to evaluate device compatibility.
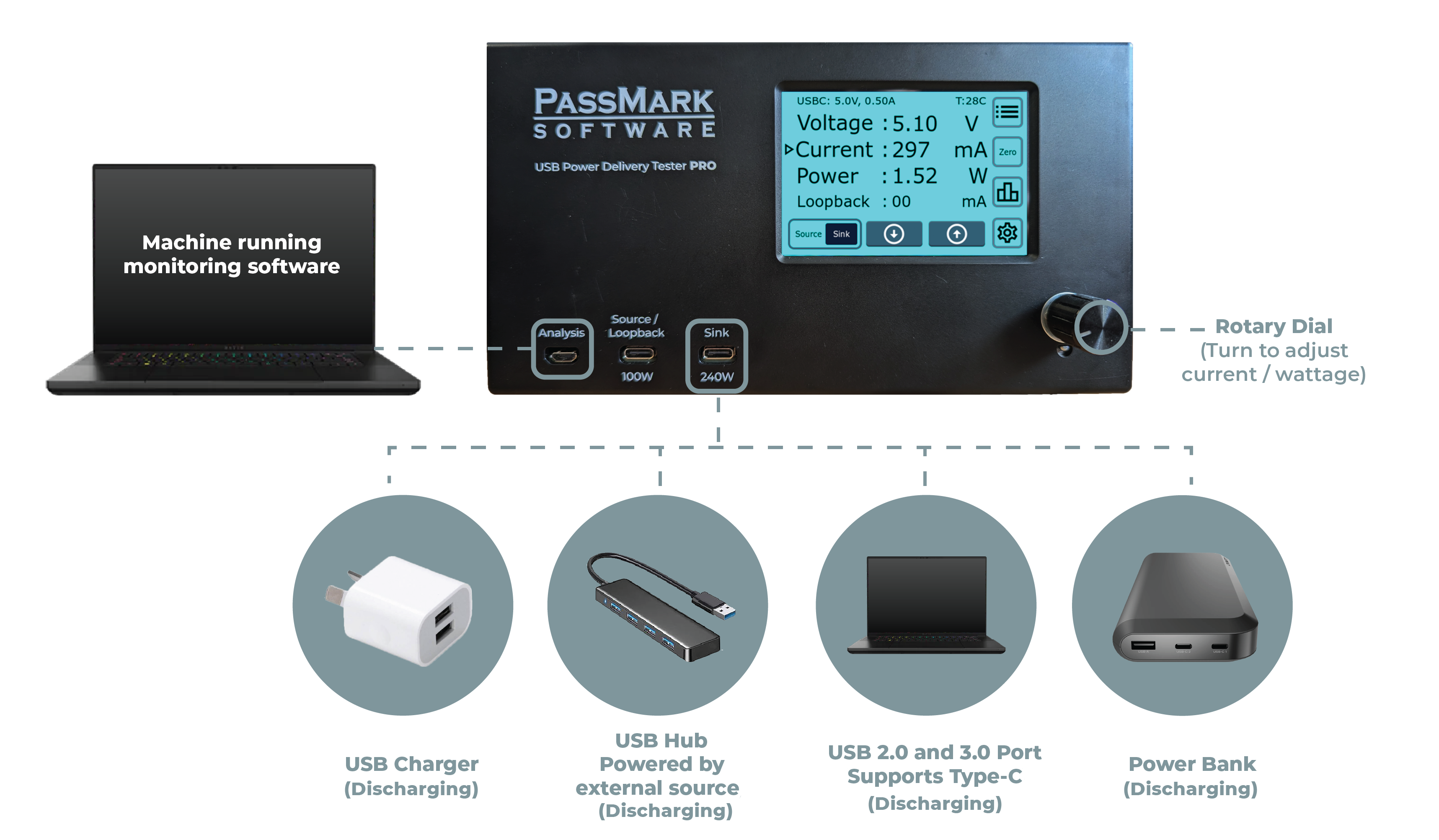
- Measure the current consumption or the power usage of USB devices such as smartphones or power banks.
- Use it with the USB 3.0 Loopback Plug, to test communication speed, data integrity, and power delivery of USB ports simultaneously.
Two Independent Ports For Emulation
Diagnose USB Power
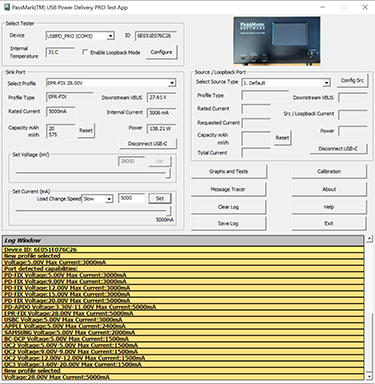
USB Power Delivery
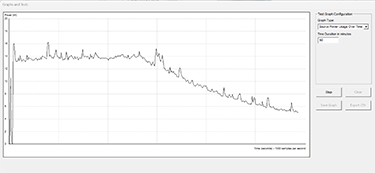
Evaluate Compliance
Safety Precautions
Do not block the air vents or restrict airflow. Ensure adequate clearance of at least 15cm around the device for proper fan operation and cooling of the unit. Also ensure there is airflow under the device.
Do not turn off the unit during high load testing, as the fan needs to operate to cool down the heatsink and the internal components.
Only use the USB PD Tester PRO with devices that claim compliance with the USB standards. A catastrophic failure of the device under test can result in the shorting of mains power to the USB cable. Which can both destroy the USB PD Tester and present a serious electrocution hazard.
Unplug the device under test from the sink or source port before turning off the unit, as some protections rely on main power.
Always have someone monitor the testing in case the device under test suddenly fails. Do not start a test and walk away.
Do not draw more current from the device than it claims to support. The port might be damaged as a result, or over current protection might lead to the port shutting down.
Some USB power supplies are known to not fully comply with the USB standards. Some also do not comply with relevant electrical standards in the countries where they are sold. Faulty or poorly designed devices can be dangerous! The USB PD Tester may expose design and manufacturing flaws in the device when putting the device under high load. The result can be catastrophic failure of the device under test. Which in turn can lead to fire, melting of the device under test, smoke, electrical shorts and even destruction of the USB PD tester PRO itself.
The USB PD Tester PRO is not a consumer device. It was designed for use by qualified electrical engineers.
Do not use with damaged with damaged cables or connectors. Replace the cable if required.